https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1238
오랜만에 올리는 문제후기!!
보자마자 알게된 것은 최단 거리 찾는 문제이다.
처음보는 도착지만 알려주는 유형이다.
그래서 처음에는 각 마을에서 출발해서 도착지에 도착한것을
하나하나 탐색해서 리스트로 저장한 다음 최댓값을 구할 예정이었다.
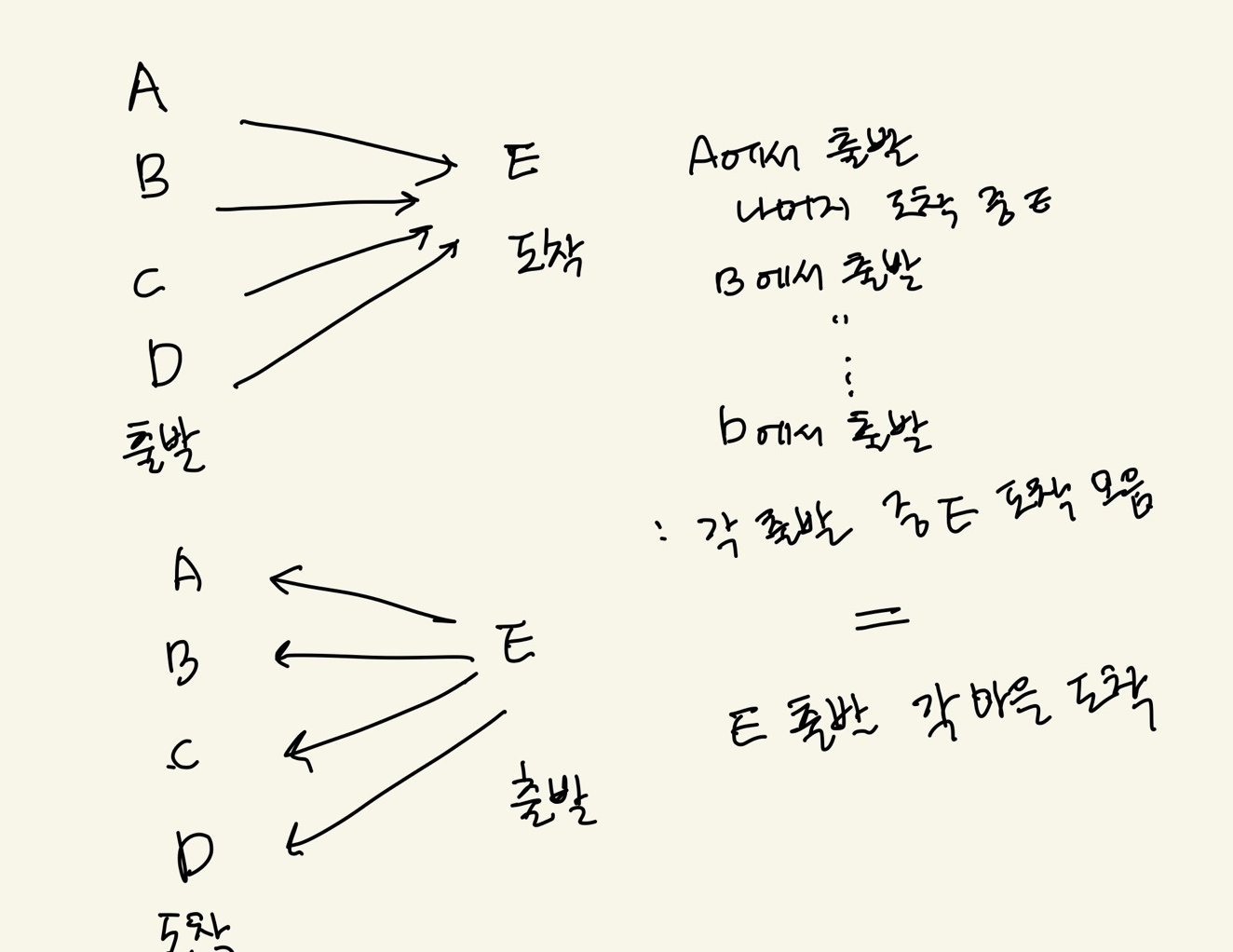
그러나 생각해보니 출발지 무작위 A 에서 목적지 B까지 걸리는 시간을 구하는 것은
B에서 출발해서 모든 마을 까지 도달 하는 시간이라는 것을 깨닫게 되었다!
와우!!
단 길이 단방향이니 반대로 그래프를 저장해 준다면 수월하게 해결 될 것 같았다.
가는 방향뿐 아니라 오는 길 또한 저장 해주어야 하니
역방향을 따로 저장 해주고
결과 또한 따로 저장해주면 A와 B 왕복의 최대값을 구할 수 있다.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Q1238 {
/*
* 원래 출발 1,2,3,4 -> x
* 하나씩 구해보려고 했는데 생각해보니
* 역방향으로 구해서 답구하는게 빠를 것 같다
* x에서 출발 1,2,3,4
*21812 264
* */
static int n,m,x,answer;
static List<List<Edge>> go = new ArrayList<>();
static List<List<Edge>> back = new ArrayList<>();
static class Edge{
int to, dist;
public Edge(int to, int dist) {
this.to = to;
this.dist = dist;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
String[] str = reader.readLine().split(" ");
n = Integer.parseInt(str[0]);
m = Integer.parseInt(str[1]);
x = Integer.parseInt(str[2]);
for(int i = 0 ; i<= n; i++){
go.add(new ArrayList<>());
back.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
int[] nums = Arrays.stream(reader.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
go.get(nums[1]).add(new Edge(nums[0], nums[2]));
back.get(nums[0]).add(new Edge(nums[1], nums[2]));
}
int[] goDist = dijk(x, new int[n+1], go);
int[] backDist = dijk(x, new int[n+1], back);
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++){
answer = Math.max(answer, goDist[i] + backDist[i]);
}
writer.write(answer+" ");
writer.flush();
writer.close();
}
static int[] dijk(int start, int[] dist, List<List<Edge>> list){
Arrays.fill(dist, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
PriorityQueue<Edge> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o1.dist - o2.dist);
pq.add(new Edge(start, 0));
dist[start] = 0;
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Edge pre = pq.poll();
if(dist[pre.to] < pre.dist){
continue;
}
for(Edge now : list.get(pre.to)){
// for (int i = 1; i <= n ;i++){
// System.out.print(dist[i] + " ");
// }
// System.out.println();
if(dist[now.to] > dist[pre.to] + now.dist){
dist[now.to] = dist[pre.to] + now.dist;
pq.add(new Edge(now.to, dist[now.to]));
}
}
}
return dist;
}
}
풀이 2 > 물론 모든 점에서 도착지로 출발하는 풀이 또한 시간 초과 없이 돌아간다
(다만 시간은 3배 메모리는 4배이다)
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Main {
static int n, m, x;
static int[] dist, distfromX;
static List<List<Edge>> e = new ArrayList<>();
static class Edge{
int to, cost;
public Edge(int to, int cost) {
this.to = to;
this.cost = cost;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] str = reader.readLine().split(" ");
n = Integer.parseInt(str[0]);
m = Integer.parseInt(str[1]);
x = Integer.parseInt(str[2]);
dist = new int[n+1];
distfromX = new int[n+1];
Arrays.fill(dist,100*m);
for(int i = 0 ; i<= n ;i++){
e.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for(int i = 0 ; i< m ;i++){
str = reader.readLine().split(" ");
int start = Integer.parseInt(str[0]);
int end = Integer.parseInt(str[1]);
int cost = Integer.parseInt(str[2]);
e.get(start).add(new Edge(end, cost));
}
int max= 0;
dijk(x);// x -> i까지
for(int i = 0 ; i <= n ; i++){
distfromX[i] = dist[i];
}
Arrays.fill(dist, 100*m);
for(int i = 1 ; i<= n; i++){
dijk(i);
max = Math.max(max , dist[x] + distfromX[i]) ;
Arrays.fill(dist, 100*m);
}
System.out.println(max);
}
static void dijk(int start){
PriorityQueue<Edge> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2)-> o1.cost - o2.cost);
pq.add(new Edge(start, 0));
dist[start] = 0 ;
while(!pq.isEmpty()){
Edge pre = pq.poll();
for(Edge post : e.get(pre.to)){
if(post.cost > dist[post.to]){
continue;
}
if(dist[post.to] > dist[pre.to] + post.cost){
dist[post.to] = dist[pre.to] + post.cost;
pq.add(new Edge(post.to, dist[post.to]));
}
}
}
}
}
'알고리즘 > java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| <java> 백준 11834 - 이진탐색 (0) | 2024.06.10 |
|---|---|
| <java> 이분탐색 사용 (0) | 2024.06.08 |
| <java> hashCode (0) | 2024.06.07 |
| <java> stack 대신 deque (0) | 2024.06.06 |
| <java> ArrayDeque vs LinkedList (1) | 2024.06.06 |